Think that you may have a urinary tract infection (UTI) but are uncomfortable with talking to your doctor about it? That’s OK. A UTI is an uncomfortable topic for discussion. Plus, not everyone has the time to drop by their doctor’s clinic.
Know that what you’re experiencing is normal and common. UTI causes more than 8 million visits to healthcare providers annually. About 12 percent of men and 60 percent of women will experience UTI at least once during their lifetime. This means that your doctor has seen many patients with your condition and if you don’t consult with a physician immediately, you increase your risk for complications.
Understandably, you have concerns regarding your UTI.
People inflicted with the condition for the first time often ask, “How long does a UTI last?” “Will a UTI go away on its own?” “How did I get UTI?” These questions, on top of your uncomfortable condition, may cause you to worry. However, excessive worrying can exacerbate your condition.
Instead, we answer the most common questions concerning UTI to inform you and put your worries to rest.
What is a UTI?

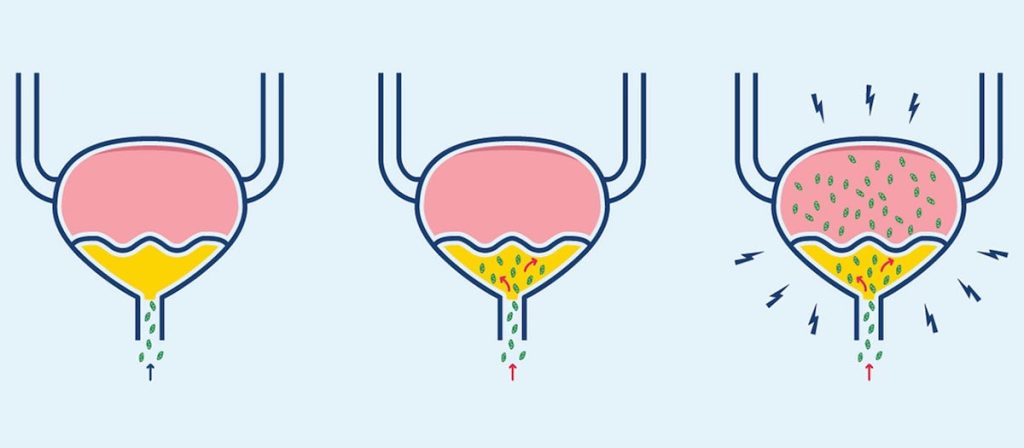
A urinary tract infection occurs when your urinary tract is infected by bacteria; on some occasions, the cause can either be fungal or viral. The infection affects your bladder, kidneys, ureters or urethra.
UTIs can fall into two categories:
- Lower tract UTIs. These are concentrated in the bladder and urethra, which are part of the lower urinary tract. If the infection is in the bladder, the UTI is described as cystitis or a bladder infection. Lower UTIs make up a majority of UTI cases and can be easily treated with antibiotics.
- Upper tract UTIs. These UTIs are more serious and rarer. Upper tract infections occur when the lower tract is left untreated. The UTI will then spread to the kidneys, resulting in pyelonephritis, otherwise known as kidney infection. This type of UTI requires medical intervention to prevent permanent damage.
Some people experience recurrent UTIs. They experience at least two infections in a span of xi months or at least three UTIs in a year.
How Did I Get a UTI? Causes and Symptoms
UTIs happen when bacteria enter the urethra and end up in the bladder. The infection begins in the bladder but if left untreated, it can affect the kidneys. In most cases, the body can get rid of UTI-causing bacteria, but there are certain conditions that increase your risk for UTIs.
The following can increase your chances of developing a UTI:
- Physical conditions. Certain conditions can increase your risk for a UTI. This list includes:
- Diabetes
- Kidney stones
- Bowel incontinence
- Bladder problems
- Frequent sexual activity. Sex increases the risk for UTIs due to the friction that occurs in your genital area during intercourse. Sexual activity promotes the migration of UTI-causing bacteria from the rectal area to your urinary tract, which eventually lodges itself in your urethra. Masturbation can do the same thing. To prevent UTIs after sex, you have to pee. The flow of urine flushes the bacteria out of the urinary tract, getting rid of the cause before it becomes a problem.
- Biological sex. Women contract urinary infections up to 30 times more often than men. A woman’s urethra is shorter than a man’s, which makes it easier for the bacteria to travel from her anus to her urinary tract.
- Genetics. If someone in your family is prone to UTI, you may also be at increased risk of UTIs.
- Age. Some studies suggest that post-menopausal women have a higher risk for developing UTIs due to estrogen deficiency and urinary incontinence, which naturally occur after menopause transition.
- Personal hygiene. Daily habits like leaving sweaty clothes on for hours, wiping back to front, not washing sex toys or forgetting to change your underwear increase your risk of UTIs.
How do you know if you have a UTI?
The symptoms of urinary infection can include:
- A burning sensation or pain when urinating
- Bloody or cloudy urine
- Strong or foul odors
- Cramping or pressure in the back or lower abdomen
- Strong urges to urinate frequently, even if you had just gone to the bathroom
If the infection has reached your kidneys, the symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Night sweats or chills and shaking
- Pain in the back, groin or side
- Reddened, warm or flushed skin
- Vomiting or nausea
- Confusion or mental changes (a symptom that is common in older people)
How Long Does a UTI Last?

Most UTIs last for less than a week, but there are different factors that can influence how long your UTI will last.
To answer “How long do UTIs last?” the first thing to consider is whether your case is complicated or uncomplicated.
How Long Does an Uncomplicated UTI Last?
According to the American Urological Association (AUA), the duration of lower urinary tract UTIs depends on how you treat it. Sometimes, your immune system can easily clear out the bacteria without the need for medications. If this is the case, an untreated UTI can last for three to seven days.
“What makes a UTI go away fast?” you might ask next. This is where antibiotic becomes a gold standard when it comes to treating your UTI quickly. Physicians often prescribe patients with antibiotics to kill the UTI-causing pathogen. They may also require a urine sample to gain a better understanding of your case. Once your lab results return (this usually takes a day or two), your physician may recommend another antibiotic to speed up the healing process.
Most of the time, antibiotics improve the symptoms of your UTI within 36 hours. This means that once you’ve been prescribed medication for your UTI, you’ll feel immediate relief from chronic pain, but not immediately cured. Even if you don’t feel the need to pee anymore, the bacteria could still be lingering around your urinary tract.
Your doctor may recommend taking antibiotics for three to five days to completely clear up your UTI. So make sure you take your meds religiously, even when you feel better. If you don’t finish the antibiotics as prescribed, you don’t eradicate the bacteria in your body. You also increase your risk for developing a strain that is antibiotic-resistant.
How Long Does a Complicated UTI Case Last?
On the other side of the spectrum, a complicated case of UTI can last for a couple of weeks. To determine if your UTI case is complex, consider the following factors:
- Whether you’re post-menopausal or pregnant
- If you have a chronic condition, like a compromised immune system or diabetes
- If the UTI is caused by drug-resistant bacteria
- If you are using nephrostomy tubes, catheters, stents or other medical devices
If you have a complicated case of UTI, you’ll need a longer course of treatment, which could include oral antibiotics and intravenous antibiotics. In general, the treatment lasts for two weeks, but you may start feeling better soon.
What Makes a UTI Go Away Fast?

Most of the time, UTIs can go away quickly. The symptoms usually stop within a day or two. As for the bacteria, it takes three to seven days (after taking your antibiotics) before they completely clear out. However, there are some things you can do to hasten the healing process:
- Stay hydrated and pee regularly. Drink plenty of water to get rid of the UTI. When you drink more water, you’ll pee more often. Every time you pee, you’ll flush out more bacteria from your system.
- Avoid caffeine. When you have a UTI, avoid drinking coffee or other caffeinated drinks for a while. According to research, caffeine can worsen the symptoms of your UTI. Best to stay away from alcoholic drinks like beers, too.
- Try pain relievers. Over-the-counter pain relievers like Tylenol or Advil can help ease the discomfort while you’re waiting for the antibiotics to work.
UTIs are common; they can happen to anyone. Fortunately, remedies are available for people struggling with this condition. As long as you attend to it immediately, you may be healed from your infection in less than a week.